Important Bitumen Tests
-
Bitumen is a substance with a variety of qualities. Bitumen tests are used to choose the best bitumen for use in road construction and other sectors.
-
Before utilizing it, during application, and after aging, bitumen tests enable us to ascertain its characteristics and assess its quality. Bitumen can also be categorized by its physical characteristics.
-
Bitumen cracks can be brought on by things like traffic and temperature fluctuations. As a result, the Bitumen's quality and lifespan are diminished. By using bitumen tests, evaluating the bitumen binder's quality, and selecting the appropriate bitumen for the necessary conditions, we can lower the risk of cracking and damage to the Bitumen.
-
Penetration, viscosity, and ductility tests can be used to determine how consistent bitumen is.
-
These testing procedures assess one of bitumen's most significant characteristics, its flow resistance. They also enable us to forecast the elasticity or hardness of bitumen at certain temperatures.
-
Tests for penetration and viscosity serve as the primary foundation for categorizing different kinds of bitumen.
-
Bitumen can be classified according to how susceptible it is to temperature changes using the viscosity test.
-
Additionally, various tests have been introduced to the industry to improve bitumen application safety. One of them that is necessary in many nations is the flash point test.
The objectives and methods of several bitumen tests are summarized below:
1. Spot Bitumen Testing
Bitumen is tested on-site to ensure that it has not been harmed by the refinery's excessive heat.
The bitumen that has cracking damage lacks the necessary stickiness to effectively hold the particles together. Additionally, it cannot withstand aging.
Procedure:
-
Put 10 ml of a solvent into a flask with 2 grams of bitumen sample to proceed. Turn the answer for five seconds. 55 seconds in a pot of boiling water should do it. Continue doing so until all of the bitumen has been dissolved.
-
Put a drop on filter paper when it has cooled to room temperature.

Bitumen Spot Test Result Negative
2. Bitumen Penetration Test
The consistency of bitumen is assessed by a penetration test. This test is used to grade bitumen according to its penetration value, or hardness.
The proper bitumen may be chosen for the specified temperature thanks to this grading system.
While softer forms of bitumen function better in cold weather, harder ones perform better in hot weather and under strong traffic loads.
Procedure:
-
A 100-gram load is inserted vertically into the bitumen with a needle during a 5-second bitumen penetration test at 25 degrees Celsius In 0.1 mm, the amount of needle movement is measured.
-
The bitumen grade increases in direct proportion to the needle's depth of penetration.
.png)
Bitumen Softening Point Testing Equipment
3. Bitumen Softening Point Test
There is no clear melting point for bitumen. The softening point is the temperature at which bitumen begins to melt. The aggregates' ability to adhere well to one another is significantly influenced by viscosity.
The bitumen gradually softens and loses viscosity as the temperature rises. Bitumen softens and loses its uniformity as a result.
Therefore, we need to understand the temperature at which bitumen begins to melt and become soft.
Procedure:
-
The ring and ball method is used in laboratories to determine the softening point. The bitumen sample is collected in two brass rings before the test is run. On top of the bitumen samples are two steel balls.
-
The assembly is heated and placed in a water bath.
-
The temperature at which a steel ball coated in bitumen strikes the base of a glass beaker is known as the softening point temperature.

Bitumen Test for Penetration -
Penetrometer
4. Test for Bitumen Ductility
The ductility of bitumen is among the significant factors that influence Bitumen quality.
A bitumen binder's ability to withstand traffic and expand and contract in response to temperature variations depends on how ductile it is. Thus, there is a lower chance of cracking, and Bitumen has a longer lifespan.
To assess the cohesive strength of the bitumen, this test involves stretching the material.
Procedure:
-
Bitumen is placed into the tester when it has liquefied. After that, the bitumen-filled tester is submerged in water.
-
It is then drawn at a rate of 5 cm/min while being cooled below its softening point. A stretched bitumen's ductility is the amount of time it takes to tear apart.

Starting of the Ductility Test

At the Time of Ductility Test
5. TCE Solubility Test of Bitumen
The inorganic content of bitumen can be determined using the solubility test. In other words, this test reveals the bitumen sample's impurity.
A high-quality building needs to employ bitumen free of contaminants.
A bitumen binder that is less than 99% soluble in trichloroethylene cannot produce stable, homogenous Bitumen.
Procedure:
Dissolve the 2 grams of bitumen sample in 125 ml of trichloroethylene to conduct the bitumen solubility test in the first stage.
Filter the solution after weighing it. The insoluble substance should then be washed, dried, and weighed one again.
Calculate the following percentage of insoluble material:
Mass of insoluble materials/mass of the bitumen sample equals insoluble matter (%).

Bitumen Solubility Test Assembly
6. Test of Bitumen's Specific Gravity
A test for specific gravity calculates the weight of bitumen relative to the weight of water in the same volume.
We can categorize bitumen because each one has a different specific gravity. Due to the fact that impure bitumen has a greater specific gravity,
specific gravity can assist in identifying bitumen impurity.
For construction, impurity is a crucial element. Poor pavement is the result of impure bitumen binder. Two techniques for figuring out
specific gravity are the Pycnometer method and the Balance method.
Here is a description of the pycnometer approach.
Procedure:
To conduct the test, take the following measurements, then utilize the equations:
-
A = Pycnometer mass
-
B = the mass of the pycnometer when it is half filled with water;
C = the mass when it is filled with bitumen. -
D = mass of the pycnometer with the material filled approximately halfway and distilled water in the remaining space.
-
E is the bitumen-filled pycnometer's mass.
Bitumen that is solid or semi-solid:
-
Specific gravity= (C-A)/[(B-A)-(D-C)]
Regarding liquid bitumen:
-
Specific gravity=(E-A)/(B-A)

Flow Diagram for the Viscosity Test
7. Bitumen's Flash and Fire Point Test
When combustible or flammable materials are heated, vapor is produced close to their surfaces. The lowest temperature at which a vapor will
ignite in the presence of an ignition source and an immediate flame is known as the flash point.
The temperature above the flash point is known as the fire point. Its flame burned for over five seconds.
Two renowned tools are used to measure the flash and firing point:
-
Pensky-Martens
-
Tester for Cleveland open cups
Procedure:
-
Fill the test cup with bitumen first for the Cleveland open cup testing. The temperature increases when you heat it. The test cup's surface
is crossed by the test flame. The sample vapor is ignited when it reaches the flash point temperature.
-
The sample is heated indefinitely until a flame appears above it to determine the fire point. The flam must burn for a minimum of five seconds.

Cleveland Open Cup System
8. Loss on Bitumen Heating Test
The percentage of bitumen volatile components is determined by the loss on heating test.
When heated for paving, bitumen samples that include a lot of volatiles become hardened, less malleable, and brittle. This type of bitumen does not
create Bitumen with a strong resistance to temperature fluctuations and traffic loads.
The loss on heating of bitumen binder in construction must be less than 1%.
Procedure:
-
50 g of bitumen sample are heated in an oven to 163 degrees Celsius in order to execute the loss on a heating test of bitumen. The bitumen
sample is then weighed.
-
The following formula is used to calculate heating loss as a percentage:
Loss on heating (%) = [(Initial weight – Final weight)/Initial weight]*100

A Shelf-rotating Oven
9. Bitumen Viscosity Testing
The bitumen's resistance to flowing is measured by the viscosity test. It flows more forcefully when the viscosity is higher.
Engineers discovered that two compounds with the same degree of penetration at 25° C perform differently at higher temperatures after
years of research and experimentation.
They felt it necessary to conduct an experiment in order to demonstrate these disparities.
The capacity of a bitumen to better compact the aggregates together to produce a homogenous Bitumen is also indicated by its viscosity.
We can determine the ideal temperature to mix and compact bitumen with aggregates by forecasting the viscosity of bitumen at two distinct
temperatures, 60° C and 135° C.
Procedure:
In order to determine the viscosity of bitumen, a sample is often placed in a viscometer, and the flow-out time is then determined under
specific circumstances. Multiply the viscometer's calibration coefficient by the time in seconds to determine viscosity.


Flow Diagram for the Viscosity Test
A Device for Testing Viscosity
10. Bitumen Drop in Penetration After Heating Test:
Bitumen's hardness and volatile content are measured using this test. Bitumen hardens when heated for building purposes because the volatile
component evaporations. As the bitumen's volatile concentration rises, so does the degree of hardness following heating.
Procedure:
-
Put the bitumen in the container to conduct the drop in penetration after heating test. Apply the needle with a 100-gram load for 5 seconds in the following step. Keep in mind that a 0.1mm scale should be used to measure penetration levels.
-
Put the bitumen sample in the oven and set the temperature to 163 °C for five hours.
-
Remove the sample after that, and allow it to cool. Repeat the penetration test in the following step.
-
Drop in penetration value (%) =
-
[ difference between 2 amount of penetration / initial amount ] * 100

Oven with a Rotating Shelf
11. Float Bitumen Test:
A highly viscous bitumen sample's consistency is evaluated using the float test. High viscosity specimens, like distillation and emulsion leftovers,
are not suitable for penetration and viscosity testing.
The consistency of the bitumen binder is essential for maintaining Bitumen's flexibility and preventing cracking.
Procedure:
-
The bitumen sample must be heated to make it flow in order to perform the float test. After that, add the sample to the collar and let it cool.
-
The alumina float is then secured by the collar. Initially, leave the entire assembly floating in a 5-degree water bath. Transfer the assembly to -
a 50° water bath once it has reached the temperature balance.
-
As the water starts to pass through the material, keep an eye on the time.
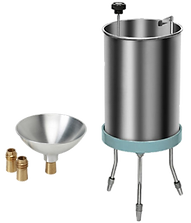
Float Test Apparatus
Overview of Bitumen Ductility Test, It's Function, and Method
Describing the Bitumen Ductility Test
One of the crucial characteristics of bitumen that demonstrates the capacity to tolerate deflections that happen on the road is ductility. As a result, there is a decreased likelihood of cracking and an extended Bitumen life duration. The ductility test quantifies ductility.
By applying stresses to the bitumen during this test, the cohesive strength is determined.
At a temperature below its softening point, bitumen is poured into the tester and pulled at a speed of 5 cm/min. The bitumen ductility is the length of stretched bitumen measured in cm before rupturing.
Typically, ductility ranges from 5 cm to over 100 cm. The bitumen ductility value should be greater than 50 cm. However, for the construction of roads, this number should be at least 100 cm.
The cohesive strength of bituminous products like oxidized and cutback bitumen can be assessed using a ductility test.
Using the IS 1208 Technique, an example of the ductility value of viscosity bitumen grades is as follows:

The Bitumen Ductility Test: Why Do We Use It?
The temperature and traffic on the roads are higher during the day. As a result, cracking will happen if the bitumen is not sufficiently ductile. Bitumen stretches and shrinks in response to temperature variations.
As a result, bitumen needs to be sufficiently ductile to resist temperature variations. Additionally, it must stick well to the aggregates and not tear under pressure from vehicles.
The penetration test is a method of determining bitumen hardness, which is inversely related to bitumen ductility. Bitumen with poor ductility characteristics will be brittle and hard..
Additionally, in hot weather, bitumen that is too soft can cause the Bitumen's surface to ripple. It is crucial to measure this attribute prior to construction using a ductility test.
International Standards for Bitumen Ductility Test Methods
The following accepted techniques can be used to conduct a bitumen ductility test:
IP 520 | ASTM D133 | ASTM D6084 | AASHTO T51 | IS 1208 | EN 13589 | EN 13703 | JIS K 2207
The following will be a description of the ductility test based on the ASTM D113 method:
Tools for Bitumen Ductility Testing
There will be a need for the following equipment:
1. Briquette
2. Pulling device with distance measuring dial
3. Water bath
4. Thermometer
5. Brass plate
6. Knife
The Ductility Test of Bitumen Procedure
-
Bitumen samples should be heated to a temperature that is 75 to 100 degrees Celsius over their softening point. Pour the bitumen into the set of briquette moulds that are positioned on a brass plate once it has totally liquefied. To keep bitumen from clinging to the brass plate, treat it with a mixture of glycerin and dextrin.
-
Put the entire set in a water bath that is held at 27 °C once the equipment has been cooled to room temperature. After that, take them out of the water bath and use a hot knife to flatten the sample's surface. Remove the plate's mould and disassemble it.
-
After setting the mould assembly in the water bath, fasten the machine with the mould clips. The bitumen moulding process must be completed properly without using any additional force.
-
Start the machine after calibrating the pointer to zero. 50 mm per minute is the continuous speed at which the clips are dragged horizontally. The bitumen thread stretches and ruptures at a certain distance, which is the ductility value.
To determine the ductility of the bitumen specimen, the three recorded values of the mould samples are averaged. In a test, the three recorded values must be within 5% of their mean value.
Bitumen Ductility Test Schematic

Pulling equipment with a dial for measuring distance

The Briquette

Show the mould in bitumen being dragged at a consistent rate in a water bath.

Note: The test is not normal if the bitumen sample reaches the water bath bottom or the water surface. To obtain a normal test, the density of the water must be increased with additions. Ductility cannot be obtained if the standard test fails. The cohesive strength of the bitumen sample is determined by the ductility test, which is performed on pure and liquid bitumen. Typically, it falls between 5 and 100 centimeters.